The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Specialities
Psychiatry
[Verbal Episodic Memory Test]
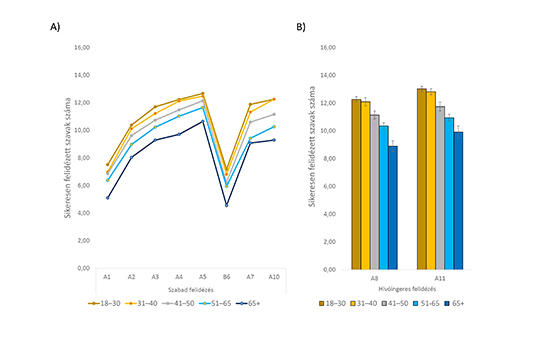
[The decline of episodic memory is one of the earliest cognitive markers of mild cognitive impairment and various types of dementia. Until today, however, there is no standardized Hungarian episodic memory test that takes into account the characteristics of the Hungarian language. The study presents the structure and standardized use of a new memory test (Verbal Episodic Memory Test, VEMT) as well as normative data in Hungary.
The VEMT is suitable for the comprehensive examination of verbal learning abilities in a broader sense, and more specifically, for the neuropsychological measurement of verbal list learning abilities. In the present study, we constructed a normative database consisting of data from 385 participants.
We showed that the VEMT is sensitive to demographic factors (e.g., age) which are linked to differences in episodic memory performance. Open access to the test is provided, and the normative scores are presented as well.
The indicators of the test are suitable for drawing a learning curve, for showing the interaction of new and previously learned information (interference effects), and for measuring differences between free recall and cued recall. Furthermore, the test scores are appropriate for distinguishing the effects of different types of memory encoding forms (phonological, semantic, and episodic), for measuring the ability to reconstruct the presentation of a sequence (memory order information), for detecting the rate of forgetting, for measuring recognition abilities, and for detecting hippocampus-related mnemonic pattern separation and completion functions. ]
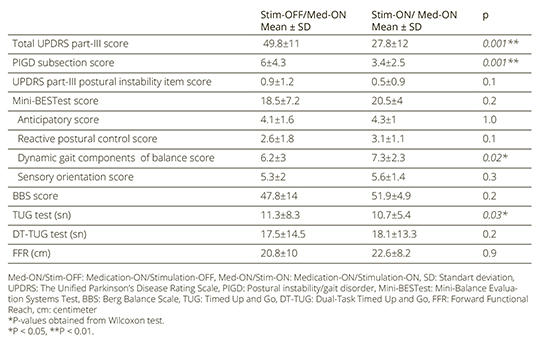
Effects of the combined treatment of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation and levodopa on balance and mobility in Parkinson’s disease
Background and purpose – To evaluate the efficacy of the combined therapy of bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation (STN-DBS) and dopaminergic medication on balance and mobility in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD).
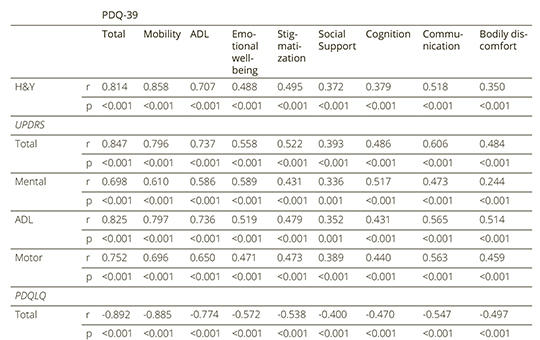
Reliability and validity of the Turkish version of the 39-item Parkinson Disease Questionnaire
This study aims to investigate the validity and reliability of the Turkish Version of the 39-item Parkinson Disease Questionnaire. A total of 100 patients with Parkinson’s disease who were admitted to the outpatient neurology clinic in Koc University and Istanbul University were enrolled. 39- item Parkinson Disease Questionnaire, Parkinson Disease Quality of Life Questionnaire, Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale, Hoehn-Yahr Scale, and Short Form Health Survey-36 were administered to all participants.
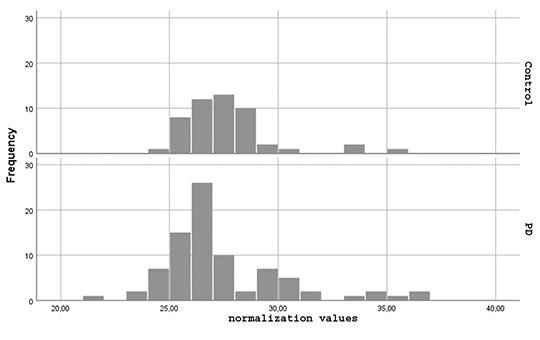
Clinical significance of serum lncRNA H19, GAS5, HAR1B and linc01783 levels in Parkinson’s disease
Long noncod- ing RNAs (lncRNAs) are highly expressed in the brain and alterations in their levels have been shown in many neurodegenerative disorders. Evidence has shown that lncRNAs play role in the onset and progression of Parkinson’s disease (PD) and it can be used as a potential therapeutic target. Our purpose was to detect whether the serum levels of four candidate lncRNAs H19, GAS5, HAR1B and LINC01783 are related with the clinical findings and treatment of PD or not.
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]
[Using patient registries is essential both in clinical research and in medical practice. Headaches, more specifically migraines are one of the most common complaints that can detract the quality of a patient’s life and these complaints also have a significant socio-economic effect. Our goal is to create a national Headache Registry and to also provide the pre-analysis of the registry’s database.
Our research is based on the national Multiple Sclerosis Registry, which we modified using the latest version of diagnostic criteria published by the International Headache Society. This clinical study contains data collected from patients suffering from migraines and currently receiving care at the Headache Outpatient Department at the Neurologic Clinic of the University of Szeged.
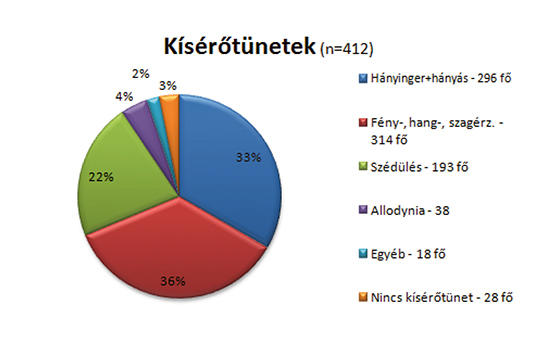
The data of 412 patients (363 women and 49 men) suffering from migraine (migraine without aura: n = 313 and migraine with aura: n = 99) were added to the Headache Registry. The average age of participants was 44.1 ± 12.5 SD years. Regarding the attributes of migraine headaches we examined the following characteristics: localization, quality and intensity (based on the Visual Analogue Scale) of the pain, frequency (the number of headache days per month), medications (acute or prophylactic), comorbidities (depression, anxiety, hypertension, asthma, epilepsy and others), family history and the occurrence of stroke among patients.
Based on international experience, patient registries are the most optimal systems for structured patient monitoring. For high level management and long-term follow up of the patients the application of registries is essential. The registries include the detailed medical history and the diagnostic and therapeutic data of the patients, and they trace the changes during the follow up medical visits. Registries are able to record the entire course of the disease in digital way. The numerous data can be set out any time from the digital database. Extensive spread of patients’ registries is fundamental not only in every day clinical practice, but also in clinical research.]
Is autism spectrum disorder an inflammation?
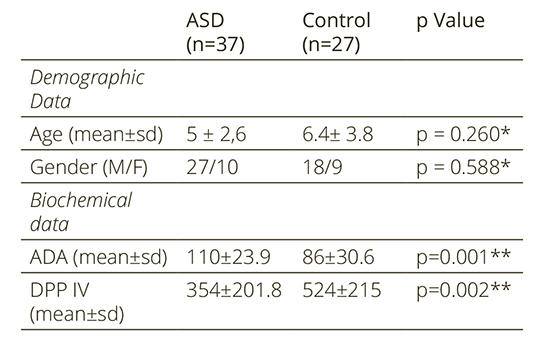
In our study, we aimed to evaluate inflammation by measuring serum Adenosine deaminase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV levels of individuals diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder and to determine its relationship with the Childhood Autism Rating Scale.
37 children aged 2-12 years with a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder and 27 children aged 2-12 years without any psychiatric disease were included in the study. Psychiatric examination and clinical evaluation according to DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder were performed on the children included in the study. The Childhood Autism Rating Scale was filled in by the researcher by interviewing the parents of the children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder. 5 ml of venous blood samples were taken from the children in both groups in the morning on a full stomach.
There was no statistically significant difference between the groups in terms of age, gender, and sociodemographic data. While serum adenosine deaminase levels were found to be statistically significantly higher in the group with autism spectrum disorder, serum dipeptidyl peptidase IV levels were found to be significantly lower. A positive correlation was found between dipeptidyl peptidase IV and Childhood Autism Rating Scale.
We think that inflammation may play a role in the etiology of autism spectrum disorder due to altered adenosine deaminase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV levels in children with autism spectrum disorder.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]1.
2.
3.
4.
5.