The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2014;24(03)
Content
[The role of hepatitis C virus in the development of non-Hodgkin lymphomas]
[There is a growing body of evidence for the association between chronic hepatitis C virus infection and certain subtypes of Bcell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The development of a lymphoid malignancy is usually preceded by cryoglobulinaemia. Here, we summarise the most important epidemiologic data, and the possible molecular mechanisms of HCV-associated lymphomagenesis. The direct oncogenic effect of the virus has not been proven, but chronic antigenic stimulation maintained by replication and viral lymphotropism might both contribute to the development of lymphomas. It should be emphasised that elimination of the hepatitis C virus can halt this process in case of cryoglobulinaemia and low-grade malignity (usually marginal zone lymphomas). In these cases, antiviral therapy might be a useful alternative of conventional immune-chemotherapy. Thus, a collaboration between haematologists and hepatologists might be a great step forward in the treatment of these diseases. It is still not established whether interferon-based short-course therapies and interferon-free regimens are also effective in the treatment of associated lymphomas.]
[Crucial points in the therapy of hepatitis C]
[The first generation of direct acting antivirals represented a milestone in the therapy of hepatitis C but other breakthroughs are on the way with imminent authorization of new antiviral drugs and interferon-free combinations. The prices of these new agents necessitate the rational use of limited financial capacities: relatively cheaper interferon-based treatments could be used first for those who can be cured with these combinations, while the most expensive treatments are to be reserved for those with no other options. In the future, interferonfree regimens will likely be used first in those patients who did not respond to firstgeneration interferon-based regimens and in whom interferon therapy is contraindicated. To avoid complications of the disease, currently it is reasonable to treat all eligible patients with advanced fibrosis, particularly those with compensated cirrhosis, with interferon-based treatments. In some instances other medical or social conditions warrant prompt treatment. The triage of treatments is based on the Priority Index in Hungary. Current triple therapies with protease inhibitors are complicated by drug and food interactions as well as by frequent (sometimes severe) side effects. General practitioners and other specialists need to be involved in managing these issues. It is of utmost importance to refer patients to hepatology care before decompensation or development of hepatocellular carcinoma. The key of timely and accurate diagnosis is organized anti-HCV screening in populations at risk and in the age group with the highest prevalence.]
[Measurement of therapeutic response during the primary systemic therapy of breast cancer]
[Primary systemic therapy (PST), also called as neoadjuvant therapy has a substantial role in the treatment of patients with breast cancer. There is an increasing need among clinicians for the monitoring of therapeutic effectiveness. Beyond simple physical examination, diagnostic imaging tools have the most important role in the measurement of the therapeutic response. Selecting the appropriate imaging method is crucial for the correct evaluation of the therapeutic response and for planning further therapy. In this paper we review breast imaging modalities currently available in Hungary and detail the efficiency of these modalities in the evaluation of the therapeutic response.]
[Meet the new member of the alprazolam family]
[The struggle against anxiety disorders and symptoms of anxiety is as old as the history of human healing. The development of anxiolytics has constituted an important field of pharmacology from the very beginning. The appearance of benzodiazepines and high-potential benzodiazepines, developed as a later evolution of the former compounds, is considered a milestone in this battle. Today alprazolam is their most widely-used representative that can be considered a golden standard. Besides its agent, the formulation of the drug is also significant, as it helps in the administration, absorption and bioavailability of the agent and even for the establishment of good compliance. Nowadays we can witness the development of medicine families containing the same active ingredient and consisting of various products. In the case of alprazolam, we can welcome a new member of the family following the immediate-release tablets and the extended-release tablets. The aim of this paper is the introduction of the new member of the alprazolam family: the sublingual tablet.]
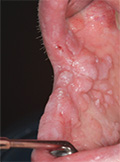
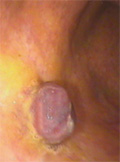
[Oral carcinoma and its preblastomatoses: the role of papillomavirus infection and the prospects of early diagnosis]
[The high incidence of oral carcinoma in Hungary is attributed primarily to tobacco and alcohol use. Recently, however, a series of publications suggested a role for humán papillomavirus in the development of oral carcinoma. For this reason we reviewed the literature regarding the associations of human papillomavirus with oral carcinoma and its preblastomatoses. We also overviewed research aiming to develop reliable methods for early diagnosis that are also suitable for screening. Early diagnosis and treatment may significantly improve the prospects of the patient. In addition, the addition of already available human papilloma virus vaccines into national vaccination programs and the extension of vaccination for both sexes may decrease the prevalence of oral carcinoma associated with human papillomavirus infection that primarily affects younger populations.]
[Analysis of the knowledge on cervical cancer and attendance indicators of cervical screening]
[OBJECTIVE - The study aims to explore knowledge on cervical cancer and cervical screening among women with 9-14 yearold daughters, and learning the attitudes towards screening, the motivation of attendance at or absence from screening. DATA AND METHODS - A quantitative, cross-sectional study was conducted using our own questionnaire in the town Nagyatád in 2012. Study participants included women who had 9-14 year-old daughters and a registered home address in Nagyatád. We received valid responses from 186 people (response rate: 75.3%). RESULTS - The interviewed women’s knowledge on cervical cancer differed significantly depending on their age, education, marital status, and economic activity. Only 45 women with higher education (p=0.043) were considered to be well informed on the subject. However, their willingness to participate in cancer screening was more favorable than their knowledge, 96.2% of the women claimed to attend an annual cancer screening. The average age of respondents was 20.92 years at first visit. CONCLUSIONS - Although the participation rate was much higher compared with that in previously published studies, it is of great importance to increase the mothers’ knowledge on cervical cancer and the factors that promote its development, so that they can pass their knowledge to their children and strengthen their protection against one of the most common sexually transmitted viral infection and the development of cervical cancer.]
[Resection of colonic polypoid cavernous hemangioma with help of rubber rings]
[INTRODUCTION - Cavernous hemangioma is a benign, rare disorder, usually localized in the distal part of the gastrointestinal system. CASE REPORT - In a 19-year-old woman treated for Crohn’s disease localized to the colon, a polypoid lesion was found during routine colonoscopy. The lesion appeared to be vascularized, purple in color and could be localized 25 cm above the anal sphincter. MSCT examination confirmed vascularization of the lesion. Considering the high risk for severe bleeding, resection was performed with surgical assistance. At first, two rubber rings were placed around the polypoid lesion. Thereafter 1 ml of epinephrine was injected into the neck of the lesion above the rubber rings, followed by polypectomy with a standard hook. No complications were present during the observation period. Histological examination of the polypoid lesion confirmed it to be cavernous hemangioma. CONCLUSION - On the basis of previous cases and the present case there might be a connection between inflammatory bowel disease and the development of cavernous hemangioma. We have not found any previous reports of a similar application of rubber rings. However, in cases where the risk of bleeding is high, this method is safe and easy to apply.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.