The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2010;20(08)
Content
[Cardiovascular prevention - Opportunities of risk reduction, 2010]
[10 years of experience following the millennium has confirmed again that data on long term cardiovascular morbidity and mortality can be influenced by effective prevention most substantially. Growing body of knowledge and experience in the field of modern cardiovascular prevention is available, but novel and novel milestone studies have been published leading to updating of guidelines, however, we cannot be satisfied with the results. Evidence suggest that despite recent efforts, Hungarian cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been reduced significantly and except for some success - acute ST elevation myocardial infarction care in accordance with the European standard - we are behind the other EU countries in cardiovascular mortality of the active (age 30-65 years) age group. Recently several interesting contradiction has been published in the field of prevention, like the effectiveness of aspirin as primer prevention, which changes our common prevention conception. Data have to be also addressed, which can explain the controversial results from a different point of view. Now we are talking about the results of REALITY study, which highlight not only the noncompliance of the patient but that of the physician as well.]
[On the safety of angiotensin-receptor blockers - A new attack on this drug class]
[Up until now, angiotensin-receptor blockers have been considered to be the safest cardio-, cerebro-, reno- and vasculoprotective drugs. In a previous metaanalysis, ARBs were accused of increasing the risk of myocardial infarction, but a number of metaanalyses and randomised, controlled trials have disproved this hypothesis. In a recent metaanalysis, ARBs were associated with an increased risk of tumours. The author reviews this issue, discusses the flaws of the above metaanalysis and, on the basis of the most up-to-date data in the literature, expert opinions and official statements (FDA, EMA), concludes that members of this drug class should continue to be used according to their approved indications, which is supported by their cardio-, reno-, cerebro- and vasculoprotective effects demonstrated in a number of appropriate, large-scale clinical studies.]
[The drug-treatment of atherosclerosis by statins]
[The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis is a complex and complicated process. The rule of some factors (lipoproteindeposition, oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, endothel dysfunction, etc) is well known, but others are not yet clarified. Conventional, metabolic and some special residual factors have also influenced for the starting process. One of them, the lipid profile is the most important. Statins are able to decrease the lipid levels - LDL cholesterol - significantly to the physiological level. These drugs are essential for the primer and secunder cardiovascular prevention moreover it is advisable to give in acute coronary syndrome as well. The most excellent statin is rosuvastatin, because of beneficial effect to decreasing LDL cholesterol level and cardiovascular events. Rosuvastatin is able to produce a regression of atherosclerotic process int he vessel walls. Presumably this effect can be explained by their pleiotrop property.]
[Clinical pharmacologic principles and problems related to the clinical use of innovative and similar biological medicines]
[The active substances in the biological medicinal products are macromolecules, primarily proteins most of which are currently produced by various biotechnological methods in different biological systems. The spatial structure of the macromolecular active substances cannot be accurately determined by the presently available methods. Therefore, both physico-chemical and biological methods are needed for the control of their quality and production. The active proteins induce immunologic reactions in the organism. The appearance of neutralizing antibodies frequently leads to the inhibition of the effect of the biological medicines. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) registers the medicinal products containing similar macromolecular active substances produced by biotechnological methods as biosimilar agents, since their chemical identity cannot be proven. The similarities and differences of their biological and immunological effects can be evaluated only in comparative non-clinical and clinical trials. The frequent exchange of biological medicines increases the appearance of antibodies in the patients, therefore the substitution of biological drugs should be done only by the treating physicians if clinically necessary.]
[Modern beta-blocker therapy from the cardiologist’s viewpoint]
[Following the publication of some large, randomised trials (LIFE, ASCOT), the benefits of the use of beta-blockers in hypertension have been questioned. On the basis of these clinical trials it has been posited that beta-blockers administered for the treatment of hypertonia are less effecient for stroke prevention. It has been suggested that first-generation beta-blockers (atenolol) have adverse metabolic effects (insulin sensitivity, lipid parameteres), which might contribute to the differences observed in clinical outcomes. On the basis of a number of clinical trials and meta-analyses performed in recent years it is now evident that the most important goal is to reach target blood pressure levels, which is usually achieved by combination therapy. Choosing drugs on the basis of strict protocols is less important. In general, beta-blockers remain one of the most important drug class for the treatment of hypertension. The author reviews the pharmacology of the cardioselective, vasodilatory drug nebivolol in detail, as well as clinical trials on nebivolol. Nebivolol has a neutral (or rather beneficial) effect on metabolic parameters (lipid parameters, blood glucose level and insulin sensitivity) as well as on left ventricular function. If hypertension is associated with cardiovascular diseases (left ventricular dysfunction, ischaemic hears disease, atrial fibrillation), nebivolol offers an excellent therapeutic alternative due to its excellent tolerability and side effect profile.]
[PErindopril-Amlodipine Reducing Blood Pressure Level Trial - The PEARL Study]
[Background and aims - In order to reach target blood pressure values more successfully and to achieve better therapeutic compliance, concomitant use of more antihypertensive agents with different mechanisms of action has gained much attention recently. In the PEARL study we investigated the antihypertensive effect of fixed dose combinations of perindopril and amlodipine (5/5, 5/10, 10/5, 10/10 mg Covercard) by measuring blood pressure values in the doctor’s office and with a 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitor (ABPM) in outpatients with primary, grade 1 or 2 hypertension, whose target values could not be reached with prior treatment. We also assessed changes of metabolic parameters and how patients felt themselves throughout the study. Patients and methods - In this open-label, multicentre, non-interventional, observational, 3 month long study we evaluated the data of 10 335 patients (5 483 female, 4 852 male, mean age: 61.0±12.4 years, waist circumference 99.0±13.8 cm). The mean duration of hypertension was 9.5±7.7 years. After signing the informed consent form, patients attended three visits (inclusion, months 1 and 3), and they were asked to fill in the data sheets (visit 1: gender, age, waist circumference, blood pressure and heart rate measured at the doctor’s office, duration of hypertension, risk factors, complications, accompanying diseases, previous antihypertensive treatments, complaints), laboratory blood tests and ABPM were optionally performed; visits 2 and 3: blood pressure and heart rate measured at the doctor’s office, adverse events, patient’s evaluation about the way they felt themselves, treatment, optionally performed laboratory blood tests and ABPM. Patients were asked to take perindopril-amlodipine fixed combination tablets in the mornings; the dose was increased if no normalization of blood pressure was observed. Data were analyzed with a one-sample t-test. The consistency of the different frequency distributions was tested with a Chi-square test. The two-sided level of significance was set at 5%. Results - All the parameters sensitive to treatment efficacy (blood pressure values measured on-site and with ABPM) were significantly improved with perindopril-amlodipine fixed combination treatment. Blood pressure measured at the doctor’s office reduced from 158/93 mmHg to 132/80 mmHg, while 24-hour mean blood pressure reduced from 145/84 mmHg to 128/76 mmHg (p<0.001), the diurnal index sensitive to blood pressure variability did not change and a dipper curve was observed throughout the study. Target blood pressure (<140/90 mmHg) was reached by 75.5 % of the patients. The mean dosage at the end of the study was 8 mg perindopril and 7.3 mg amlodipine. The results were consistent across subgroups of different previously received treatments and cardiovascular risks. Regarding laboratory findings, the reduction of total cholesterol from 5.67 to 5.21 mmol/L and that of LDL cholesterol from 3.18 to 2.83 mmol/L (p<0.001 for both) were of clinical importance. Eighty-five percent of the patients evaluated the way they felt themselves as excellent or improved. No serious adverse events were reported. Conclusion - Perindopril-amlodipine fixed combination can be administered effectively and safely to a large population of hypertensive patients who do not reach target blood pressure values.]
[A chance to concretize the teratogenic risk: healthy babies born to mother with isotretinoin treatment during pregnancy]
[The teratogenic risk means the probability of the occurrence of congenital abnormalities in fetuses after the exposure of teratogenic agents, mainly drugs during pregnancy. The recent highresolution ultrasound scanning may help us to concretize this teratogenic risk. The Genetic, Teratogenic and Family Planning Counseling Clinic of the authors in Budapest were visited by 10,557 couples or client between 1998 and 2007. Ten pregnant women visited this Clinic due to the isotretinoin (Roaccutan) treatment during pregnancy during the 10 years study period. At present Roaccutan is the most teratogenic drug among the medicinal products in Hungary because its teratogenic risk is 25% for a characteristic pattern of congenital abnormality syndrome including a/microtia, ventriculomegaly and contruncal cardiovascular malformation. These fetal defects are detectable by the high-resolution ultrasound scanning between 18th and 20th gestational week of pregnant women. Thus this examination was recommended for the 10 pregnant women with unintended use of isotretinoin (Roaccutan ) in early pregnancy. Six pregnant women followed our advice and the repeated ultrasound scanning was not able to detect the above-mentioned characteristic defects and all the 6 newborns were healthy after birth. In conclusion the recent highresolution ultrasound examination provides a chance for the diagnosis of certain fetal defect between 18th and 20th gestational week of pregnant women. The Hungarian law allows these pregnant women to decide the termination of pregnancy until 20th (24th) gestational week after the diagnosis of severe fetal defects. However, this approach can protect the life of the major part of fetuses in pregnant women at high risk.]
[Group therapy for alcohol-dependent patients using autobiography reconstruction]
[A group therapy method was built on results of previous researches using narrative psychological approaches. Our primary technic was narative restructuring. Alcohol addicted patients’ language expression mode of their autobiographies was modulated similar to recovering ones’. We supposed it had therapeutic effect, that could be measured by the Hopelessness Scale (HS) and the Means Ends Problem Solving Test (MEPS). We recorded the tests before and after the therapeutic process, and the differences of their datas were compared (t-test) to similar ones from control persons, who participated in any other group therapy. Significant difference was experienced. Our method reduced hopelessness and increased problem solving more effectively, than other group therapies.]
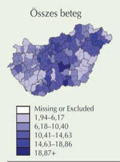
[Need-adjusted inequalities in the use of healthcare in Hungary]
[INTRODUCTION - The reduction of need-adjusted inequalities in the use of healthcare results in higher efficiency and fairer allocation of resources. PATIENTS AND METHODS - Data for all patients who received inpatient care (same-day or hospital treatment) in 2007 were used in the analysis. Beyond the diagnostic and diagnosisrelated group’s weight information and the number of inpatient days, the patients’ record contained data on age, sex, and postal code of residency. Besides personal data, socio-economic characteristics and general indicators of healthcare capacity have been included in the applied multilevel statistical analysis. Inequalities were estimated for all patients, and separately for those treated for malignant tumour, cardio-vascular diseases, or other diseases. RESULTS - Significant regional inequalities were observed in one-day care but an order of magnitude less in longer inpatient care. Comparing the two major diagnostic groups, the inequalities were greater among patients with cardiovascular diseases than for those with cancer. Only a small fraction of the observed inequalities was explained by the differences in the composition of population of small regions. The inequalities in the use of healthcare were largely explained by socio-economic characteristics of the regions. CONCLUSIONS - Need-adjusted inequalities in the use of healthcare supported the hypothesis that efficiency of the Hungarian healthcare system can be significantly improved by allocating the available resources according to the patients’ need.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.