The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2003;13(03)
Content
[Extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel diseases]
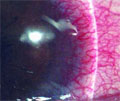
[Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are systemic disorders. Bowel symptoms are the predominant manifestations, however during the course of the disease a lot of intestinal and extraintestinal complications may occur. Systemic complications are responsible for substantial co-morbidity and they have negative influence on the quality of life. A part of the extraintestinal symptoms seem to have common pathogenetic background with IBD, while others are the consequences of subsequent metabolic and endocrine abnormalities or may relate to local complications and adverse effects of treatment. Growing evidence is available on the role of genetic and immunologic factors in the pathogenesis of extraintestinal manifestations. Most important systemic complications are: peripheral and axial arthritides, osteoporosis, uveitis, erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangraenosum, primary sclerosing cholangitis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, different types of anaemia, thromboembolism, kidney stones and urinary complications. Cooperation with the specialists is very important in the diagnosis and treatment of these comlications. During followup of IBD patients special attention is needed to monitor possible extraintestinal manifestations.]
[Benefit of combined clopidogrel-aspirin platelet aggregation inhibition in acute coronary syndrome and after percutaneous coronary angioplasty]
[Platelet aggregation inhibition is equally important both in conservative and interventional cardiological treatment of acute coronary syndrome. Recently, results from three important trial were published. All three proved the efficacy of the combined aspirin + clopidogrel treatment. The basic results of the three clinical trials (CURE, PCI-CURE, CREDO) are summarized in the article. In the CURE trial the combined primary endpoint was reached in 11.4% of the patients in the control group and in 9.3% in the clopidogrel group. The relative risk reduction was 20%. The combined primary endpoint included CV mortality, MI and stroke. The treatment effect was mostly detectable in the prevention of MI and stroke. In the PCI-CURE trial 2658 patients of the CURE trial were analysed. All of them were treated by coronary angioplasty. In this group the primary endpoint (CV death, nonfatal MI, urgent revascularisation) was reached in 6.4% of the aspirin treated and in 4.5% of the aspirin + clopidogrel treated patients. The relative risk reduction was 30%. The CREDO trial investigated patients after coronary angioplasty. The indication of angioplasty was either acute or chronic. All patients received combined aspirin + clopidogrel but only for four weeks in the control group or for one year in the treatment group. The combined primary endpoint was decreased by 26.9%. In all the 3 trials the risk of bleeding was slightly but significantly increased by the combined aspirin + clopidogrel treatment. Clinical application: based on the results of the 3 trials it is concluded that combined aspirin + clopidogrel treatment is indicated in all patients with acute coronary syndrome, independently from the treatment strategy. The treatment should be continued for one year. This is also applicable for all patients treated with coronary angioplasty.]
[Pacemaker therapy - New indications]
[This article details the classical and newer clinical applications of pacing, i. e. the use of permanent pacing for patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, prevention of atrial fibrillation and pacing in long QT syndrome. The cornerstone of definitive pacemaker therapy is the establishement of correct indication and the optimal selection of pacemaker modality which significantly improve the quality of life of patients. The use of combinations of sensors balancing the strengths and weakness of each represents a logical step toward the optimization of rate responsing pacing. Reliable automatic functions have been incorporated in modern pacemakers to improve the efficiency and quality of life of patients.]
[Proteomics - the new challenge]
[The term ”proteome” (proteome, PROTEin complement to a genOME) by now a generally accepted expression in biomedical science meaning a complete complements of proteins. The discipline ”proteomics”, coined after proteome, deals with the analysis of the complete set of proteins occurring in the living organism. This includes the identification and quantification of proteins, the determination of protein localisation, modifications, interactions, activities and function. Performing comparative studies is an important part of proteomics for the analysis of proteins in health and disease. The knowledge generated is already used for improved diagnostic procedures and development of new drugs and therapies. During the proteome analysis, as outlined in this paper, even very small quantities (concentrations) of proteins are measured, then the protein is identified and its structure is elucidated. This procedure is followed by functional studies. An important part of proteomics is the collection and validation of numerical databases suitable for data mining. There is a general understanding that methodology driven research (e.g. NMR, mass spectrometry, DNA chips) is also an integrated part of this discipline. It is already sensed that the analysis of proteome can lead to the discovery of new proteins proving targets for drug research and to the establishment of new procedures with a perspective of improved diagnosis and therapy.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.